What is medicinal cannabis?
Medicinal cannabis is cannabis that is used for any therapeutic purposes. This includes cannabis products in any form (pharmaceutical preparations, cannabis extracts, oils, tinctures, and dry flower) to help treat or relieve symptoms of an expanding list of medical conditions.
Is medicinal cannabis legal in Australia?
Yes, in 2016 the cultivation and use of any parts of the cannabis plant for medical purposes was legalized in Australia.
However, you can’t simply go to a doctor, obtain a prescription, and fill it at a pharmacy as you would with conventional registered medicines. Most cannabis-based medicines do not appear on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG), and require approval from the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) and the relevant State or Territory’s Health Department. Learn more here.
Did you know, there have been over 120,000 prescriptionsfor medicinal cannabis approved by the TGA up to May 31, 2021.
What are the main forms of medicinal cannabis?
There are many different types of medicinal cannabis that differ in cannabinoid profile, strength, formulation and quality.
Read our blog what to look for when selecting a CBD or medicinal cannabis product.Medicinal cannabis products are available as:
- Capsules
- Chewables/”gummies”
- Creams/ointments
- Flower
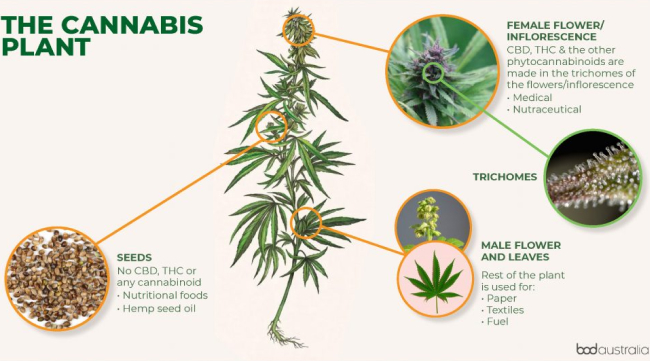
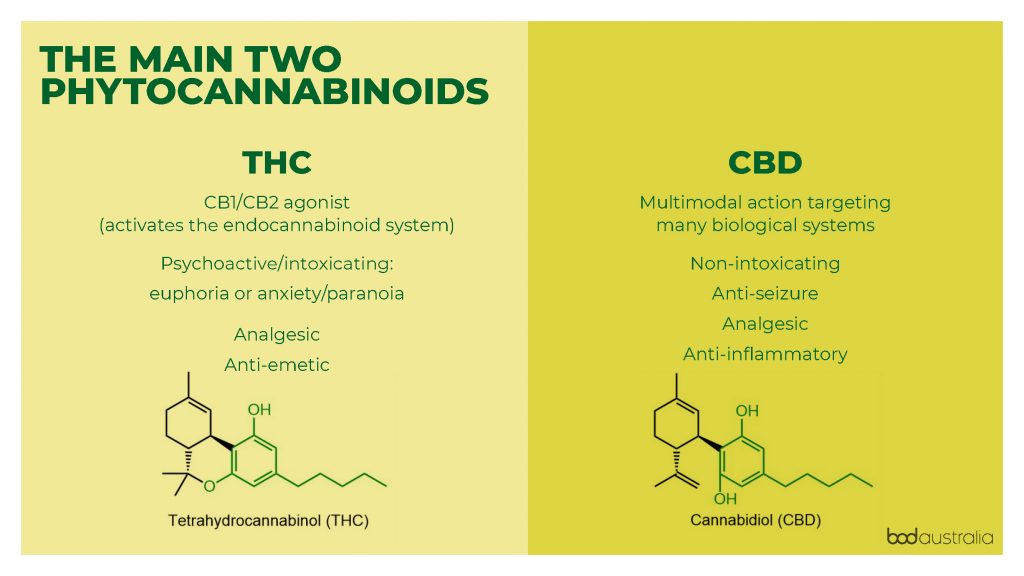
What is the difference between THC and CBD?
THC and CBD are the two most abundant cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. Although they look similar, they have different, sometimes opposing, actions in the body. For example, THC can have intoxicating effects at high doses, while CBD does not. While they both have medicinal properties, the risk of THC’s intoxicating effects makes it less desirable as a functional medication and therefore CBD has grown in popularity as a compound to be explored for medicinal properties.
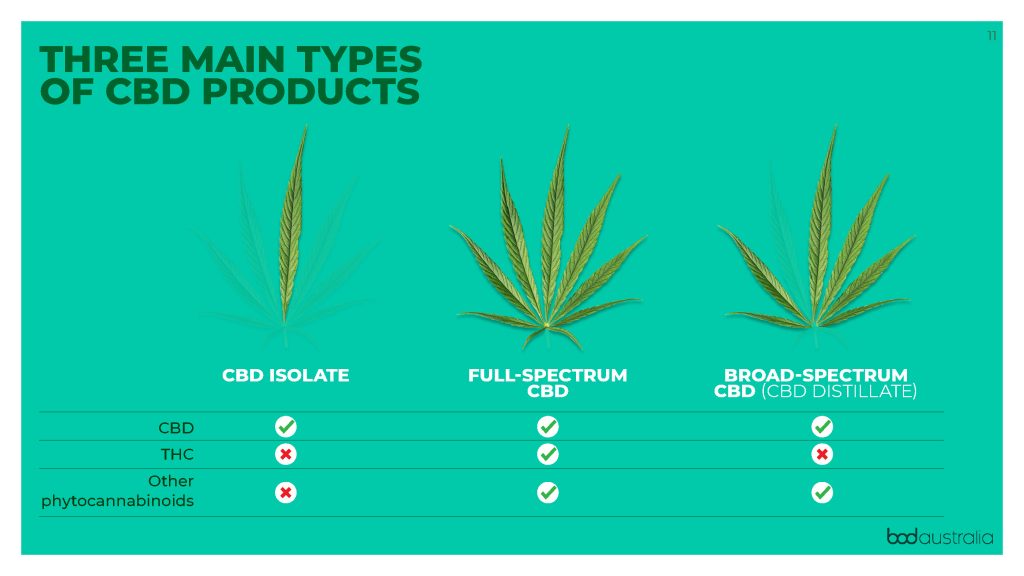
For cannabis oils (the most common format) there are three main types:
- Cannabinoid isolate, which contains only THC or only CBD at different concentrations
- Full-spectrum extracts, providing a large range of cannabinoids and other plant constituents at different concentrations. These products are typically high in THC or CBD and have lower levels of the other lesser-known minor phytocannabinoids.
- Broad-spectrum extracts, do not contain the full range of constituents naturally present in the starting plant material. Instead, the extract is manipulated to remove or add specific plant constituents. Typically THC will have been removed.
How does medicinal cannabis work?
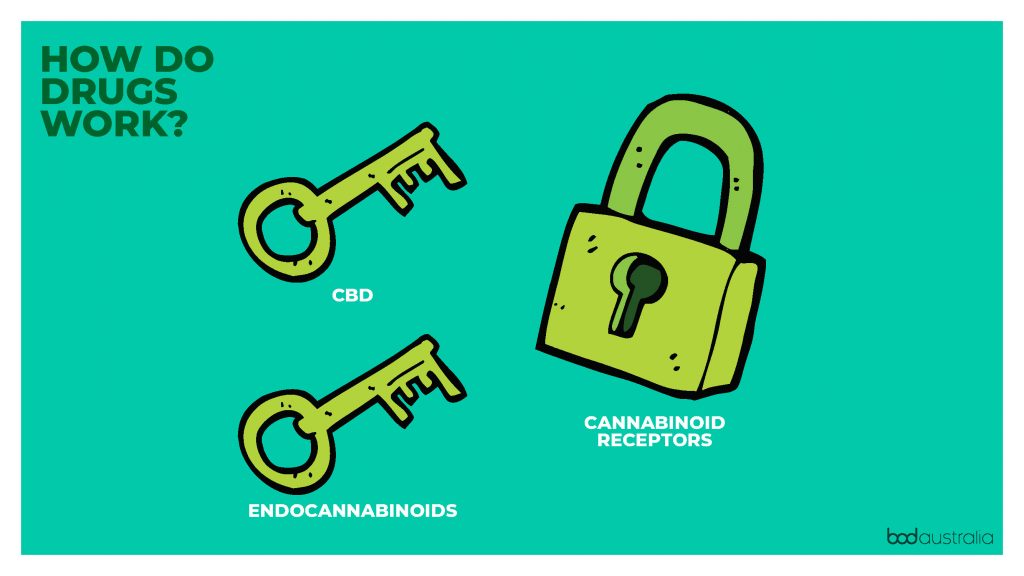
Did you know that your body makes its own cannabinoids?
They are called endocannabinoids!
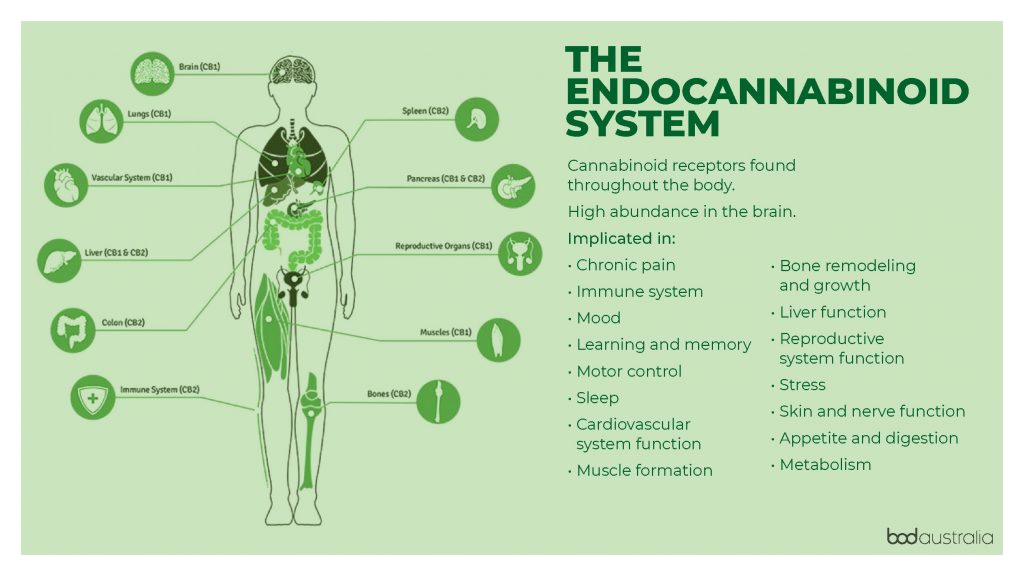
The endocannabinoid system helps regulate many different functions, including memory, mood, pain, appetite, inflammation, and metabolism to name a few.3
What conditions can medicinal cannabis be used to treat?
In Australia, because it is still an unapproved form of treatment, the TGA will need to assess each request for prescription and determine if there is sufficient evidence to support its use. Medicinal cannabis may be prescribed for a broad range of conditions due to its action on the endocannabinoid system, and other systems and research into its potential therapeutic benefits continues to grow.
How to get medicinal cannabis?
Any medical doctor can prescribe medicinal cannabis in Australia with the approval from the TGA and the relevant State or Territory’s Health Department. Find out more about the process in our step-by-step guide.
Want to know more?
Follow us on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter to stay up to date with latest news, education and research.
Important: the information on this page is intended for educational purposes only. This information is not intended to be used for medical advice or any other purpose. Individuals should always consult with their doctor and other healthcare professionals on the most appropriate management of their health needs.


